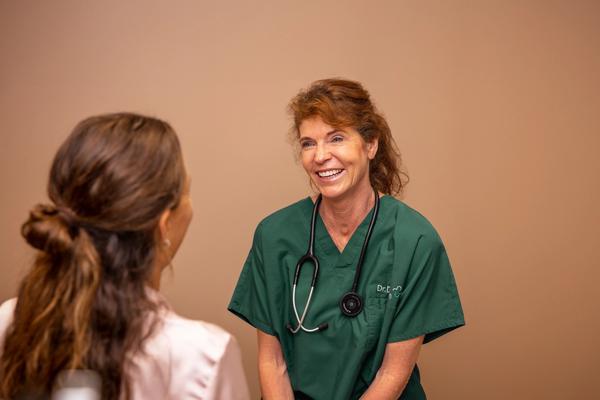
HPV (human papillomavirus) is a group of viruses that, among other things, are sexually transmitted and are a very common infection in women. Fortunately, the infection usually goes away on its own. Most have no symptoms and in nine out of ten, the infection goes away on its own within 6-24 months.
– Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is the most common sexually transmitted infection we have. Of all sexually active people, over 70 per cent get this virus, so it is more the rule than the exception to get infected, says doctor Daniel Sørli.
There are around 200 different HPV viruses, and they all spread through direct contact. About 40 of these are transmitted through sexual contact. HPV is the only known cause of cervical cancer, with types 16 and 18 causing 70% of these. Some types of HPV cause benign genital warts. Most Norwegian women and men become infected with HPV during their lifetime. The virus can be present without being active for several decades before it becomes active and causes infection, so you can be a carrier of this virus for a long time without even being aware of it.