Melanoma (Mole Cancer)
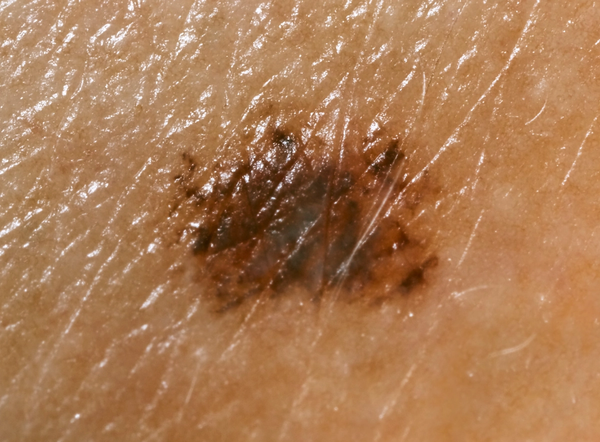
Melanoma, also known as mole cancer, is the most serious form of skin cancer. Early detection and treatment are essential to combat this disease.
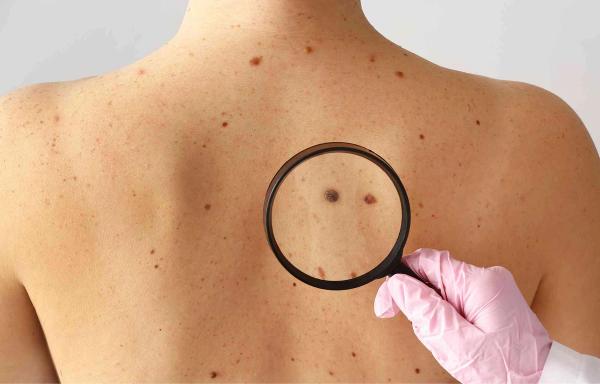
At Dr. Dropin, we offer thorough mole examinations and quick access to experienced skin specialists.
Read on to learn more
See available hours at the dermatologist