Genital warts
Genital Warts - Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
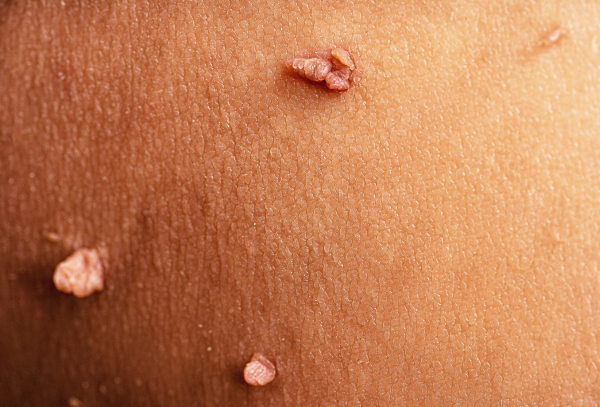
Genital warts, or condylomas, are small benign growths located on the genitals, the area around the anus or in the cervix. Genital warts are caused by a virus called human papillomavirus, often referred to as HPV, and is transmitted through sexual contact. The warts usually disappear on their own after 6-12 months, but if they cause problems or are a nuisance, they can be treated locally with various means on the recommendation of a doctor. If you have typical symptoms of genital warts, you can now get a self-service prescription.
Get prescription 295,–